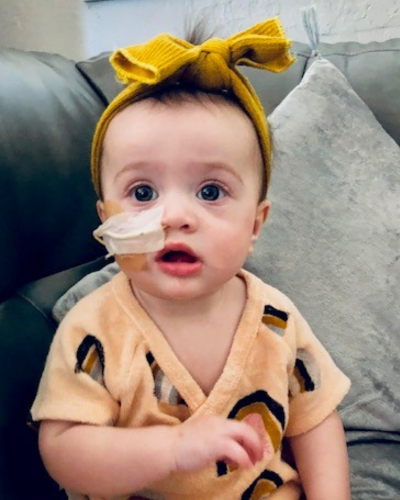
Pediatric Feeding Disorder to ARFID: A Young Child’s Journey
Published by Feeding Matters on Jun 26, 2023
Not long after Alexandra Marcy’s third child was born, she knew something was wrong with her eating. From the start, her daughter, Emerson, wasn’t latching properly. “I was told at the hospital that her latching would come naturally. We tried for a few days, and I knew it wasn’t normal,” she says.
It wasn’t long before Emerson’s diapers were dry.
A doula friend suggested Emerson might have a tongue tie, making it hard for her to latch. Not only did she indeed have a tongue tie, but she also had a lip tie and a buccal tie – a cheek tie that results from an abnormally tight frenum. Emerson underwent a laser procedure on all three, and Alexandra started using a nipple shield while breastfeeding.
Even then, says Alexandra, “She’d get a little bit of milk but never enough. Any time I tried to nurse her, she’d scream.”
Those early feedings began a four-year feeding journey that’s still developing today. What began as a medical feeding issue then is today a psychological issue. The Marcy family continues to navigate the uncertain path between pediatric feeding disorder (PFD) and Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID).
Click here to read about PFD and ARFID and how the two diagnoses can overlap.
See here why misdiagnosing PFD and ARFID can do more harm than good.
Following is their story.
One young child’s journey from PFD to ARFID
Alexandra gave up on breastfeeding early and instead pumped milk for Emerson. The baby never took more than an ounce at a time. Even then, Emerson would spill milk out of her mouth and gag. Like many parents of children with PFD, Alexandra spent most of her time around the clock pumping and feeding her daughter.
Emerson also sounded congested all the time. Her pediatrician assured Alexandra this was normal.
Alexandra wasn’t convinced, and at three months, baby Emerson was breathing strangely and seemed limp. It was RSV season, but a swab and an X-ray seemed fine. But Emerson hadn’t gained weight since her previous pediatric appointment. When Alexandra returned a week later for a weigh-in, the baby lost a few ounces. The pediatrician recommended Alexandra supplement with formula. He suggested her breast milk wasn’t fatty enough. Emerson lost more weight even with formula.
They ended up at Phoenix Children’s Hospital (PCH) when Emerson was four months old. “I saw so many doctors, who all thought her breathing and eating will be fine. We were there for over a week without any answers,” says Alexandra.
It wasn’t until Alexandra, who worked in a therapy clinic, managed to connect with a feeding therapist from her team that she got some answers. She looked over Emerson’s original X-ray of her lungs from when Alexandra suspected she had RSV and saw shadows in the image. A second X-ray showed the shadowing had gotten worse since then. This was a sign the baby was aspirating.
The family turned to a gastrointestinal doctor for answers. Emerson was diagnosed with allergies and started an animos-based formula, which helped. “Still, though, she was a terrible eater. It was hard to get 4-oz. into her,” says Alexandra.
It seemed like any time Emerson would make some feeding progress with her feeding therapist, she would get an upper respiratory infection or rotavirus that would set her back.
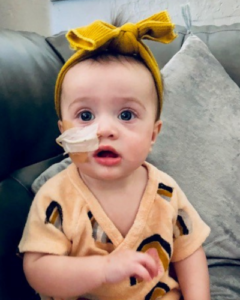
Emerson got an NG tube to build up her strength. The NG tube helped the baby gain weight, but Alexandra still remembers it as traumatic. “Any time it came out, I’d have to have my eight-year-old hold her down while I put it back in her. It felt crazy and sad.”

Eventually, Emerson was diagnosed with:
Type 2 laryngeal cleft: An abnormal opening between her larynx and the esophagus that allowed food to enter her lungs
Tracheobronchomalacia: Her weak tracheal or bronchial tubes would collapse any time she ate or cried.
Dysphagia
“Finally, we had answers, but no way to fix it,” says Alexandra.
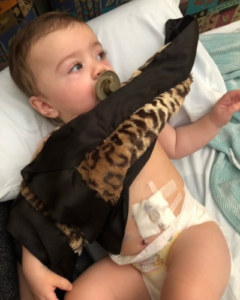
At eight months, Emerson transitioned to a G-tube as a long-term feeding solution. “This was so much better because I could see her beautiful face. She wasn’t gagging and throwing up,” says Alexandra.
The G-tube even helped Emerson overcome some food aversions to try solids. Alexandra added her to the months-long waiting list to get into the feeding program at PCH.
Thanks to the family’s hard work, Emerson progressed and eventually got into the feeding program. But at age three, she started to regress again. She stopped eating most of what her parents offered, accepting only four foods.
Even after three weeks in an intensive feeding therapy program at PCH, Emerson wasn’t progressing. At that point, all her medical issues had been addressed and resolved.
The hospital team suggested Emerson see a psychologist, who thought the three-year-old could have ARFID. Eventually, Emerson was diagnosed with ARFID and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). She was young for both psychological diagnoses, but a child psychologist and a child psychiatrist agreed.
Emerson was treated with EMDR therapy to help her reprocess the medical trauma she experienced as a baby and toddler. “Any time she eats, she doesn’t want to feel pain, so this makes her restrictive and gives her intrusive OCD thoughts,” says Alexandra.
A psychiatrist who has worked with many children with PFD and ARFID prescribed medication, helping Emerson be more open to new foods and eat more. Things have gotten easier, but still, says Alexandra, their journey isn’t over. “She just doesn’t care about food. She doesn’t act hungry, and I have to remind her to eat.”

Alexandra hopes sharing her family’s story will help others navigate a similar path.
For more information, visit Feeding Matters’ resource page: PFD and ARFID. If you are a parent needing support, check out our family support resources .